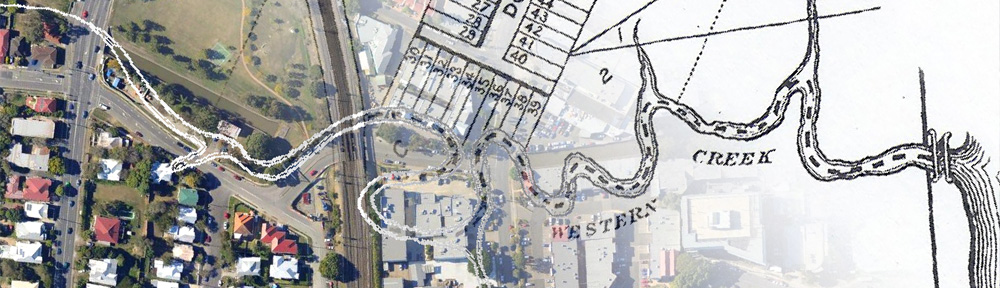
This is the first in a series of posts about Langsville Creek, which was Western Creek’s upstream neighbour on the Toowong/Milton Reach. I do not intend to research Langsville Creek fully at this stage, as I have too much still to learn about Western Creek. But I couldn’t resist tracing the path of this (mostly) lost creek and seeing what can be learned by looking at the some of the old maps and aerial photographs. Each post will look at a different part of Langsville Creek. This one focuses on the lowest reaches of the creek, near where it met the Brisbane River. You can also now read Part 2 and Part 3 of the series.
The meanders of Moorlands
Toowong Cemetery … Anzac Park … the Mount Coot-tha Botanical Gardens … Quinn Park … the McIlwraith Croquet Club … Toowong Memorial Park … Moorlands Park.
What do all of these places have in common? The answer is a creek. Not a creek you are likely to have seen or heard of, for there are few traces of it left today. But there once was a creek that flowed through all of these locations.
The creek uniting these locations was known to early Brisbanites as Langsville Creek, though I imagine that it also had names given to it by the Turrbal people long before Europeans arrived. I’ve not read up on how and when it came to be known as Langsville Creek, but given that just about everything else in this part of Brisbane is named after John Dunmore Lang, I’m going to take a punt and guess that this creek was as well.
You can see Langsville Creek — or at least part of it — on the early maps of Brisbane. It’s depicted most clearly on McKellar’s 1895 map, the relevant portion of which is reproduced below. The creek itself is unnamed on this map, except by way of the bridge that crosses it where Patrick Lane meets the River Road (now Coronation Drive). The creek looks rather like an outgrowth of the river, as if the river has put out tentacles or feelers, each one meandering through the landscape much as the river winds its way to the bay. The land surrounding it appears to be mostly undeveloped, presumably because it was damp and flood-prone.
Continue reading